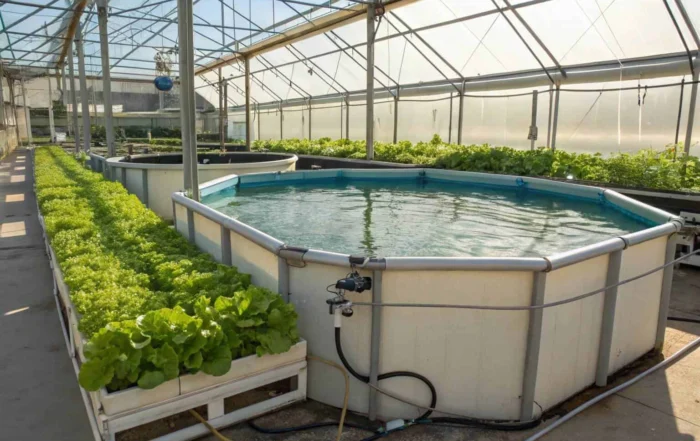
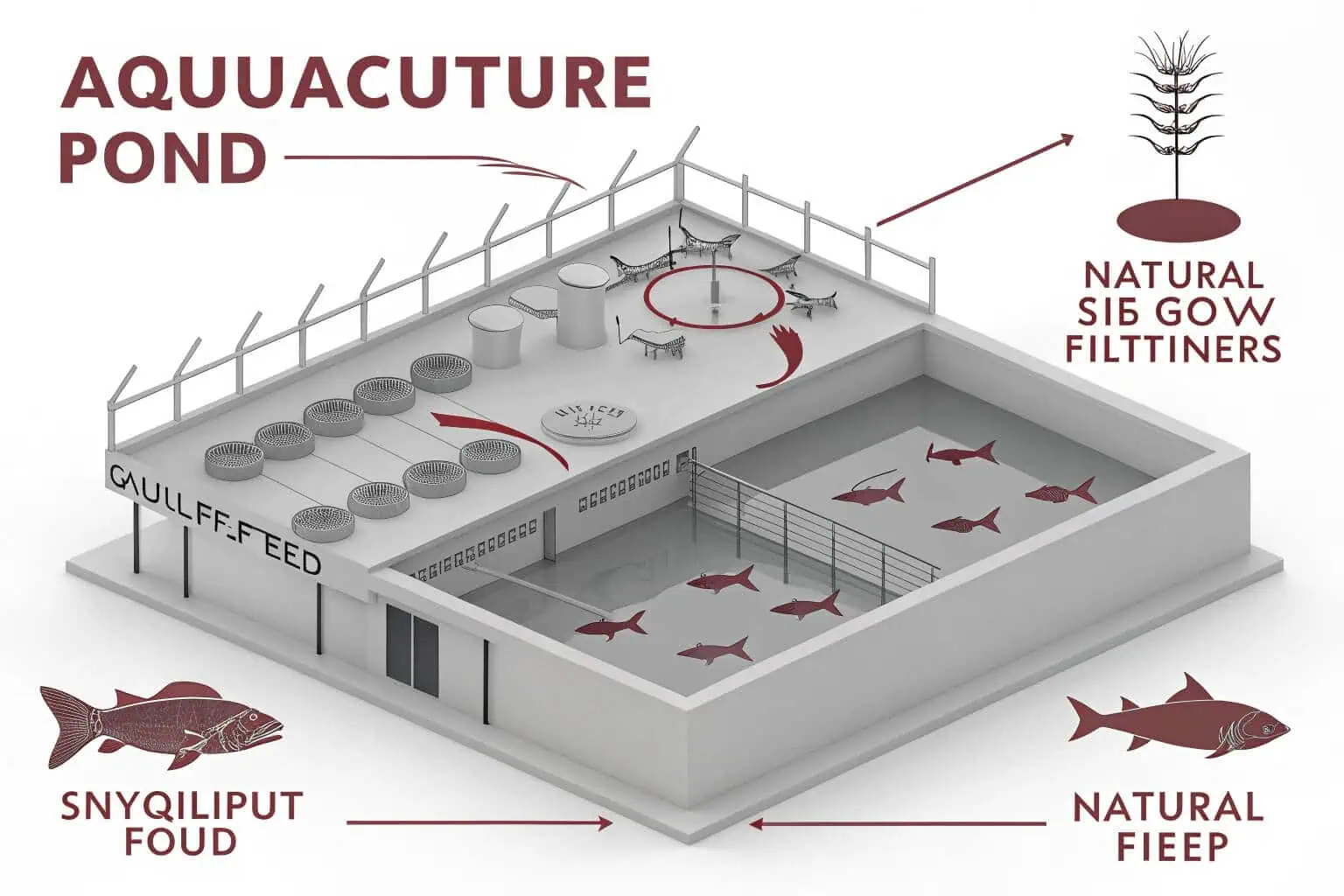
Thinking about fish farming but don’t know where to start? The options seem complex and expensive. A pond system is the simple, effective solution you need.
Pond system aquaculture is a method of farming aquatic organisms like fish and shrimp in natural or man-made ponds. It creates a controlled environment that mimics a natural ecosystem, allowing for efficient, large-scale production with relatively low initial investment, making it highly accessible for beginners.

I’ve seen many people get into aquaculture with big dreams, only to stumble because they overlooked the fundamentals. Understanding what a pond system truly is—beyond just a hole filled with water—is the first step to success. It’s about creating a balanced, living environment. Let’s break it down further.
What is the pond system in aquaculture?
You hear "pond system" thrown around in aquaculture circles. It sounds simple, but what does it really involve? It’s the backbone of successful fish farming.
In aquaculture, a pond system is a complete setup for raising aquatic life. It includes the physical pond, water management tools like aerators, and the biological community within it. This system is designed to control water quality, provide food, and protect fish from predators for optimal growth.

When I first started exploring aquaculture, I thought a pond was just a pond. But a "system" implies much more. It’s an entire ecosystem1 you manage. It’s not just about holding water; it’s about creating a productive environment. Let’s look at the core parts that make it work.
The Physical Structure
This is the pond itself. It can be an earthen pond dug into the ground or a structure made with liners, like our PVC-lined tanks2. The size and shape matter a great deal. They affect water circulation3, temperature, and how easily you can manage and harvest the fish. A poorly designed shape can create dead spots where water doesn’t circulate, leading to low oxygen and waste buildup.
Water Quality Management
This is where many beginners fail. A pond isn’t a sealed box. Fish produce waste, and uneaten food decays, creating toxic ammonia. You need tools like aerators to add oxygen and sometimes filters to clean the water. I’ve seen yields double just by adding a simple aeration system4. Regular monitoring of parameters like pH, ammonia, and dissolved oxygen is not optional; it’s essential for preventing disaster.
The Biological Components
This includes the fish you’re growing, but also the phytoplankton and zooplankton that serve as natural food. A healthy pond system5 balances these elements. It’s a bit like gardening; you cultivate the water to feed your crop. This natural productivity can significantly reduce your feed costs and is a sign of a healthy, stable system.
What is the definition of an aquaculture pond?
Is any body of water an aquaculture pond? This confusion can lead to costly mistakes. A true aquaculture pond is a purpose-built environment, not just a puddle.
An aquaculture pond is a man-made body of water specifically designed and managed for growing aquatic organisms. Unlike a natural pond, every aspect—from its depth and shape to its water source and drainage system—is controlled to maximize production and maintain a healthy environment for the stock.

I often get asked what separates a farm pond from a simple water hole on a property. The difference is intention and engineering. An aquaculture pond is a tool for farming, and like any good tool, it must be designed for its job. It is an asset that you build and manage for a specific outcome: growing healthy fish6 efficiently.
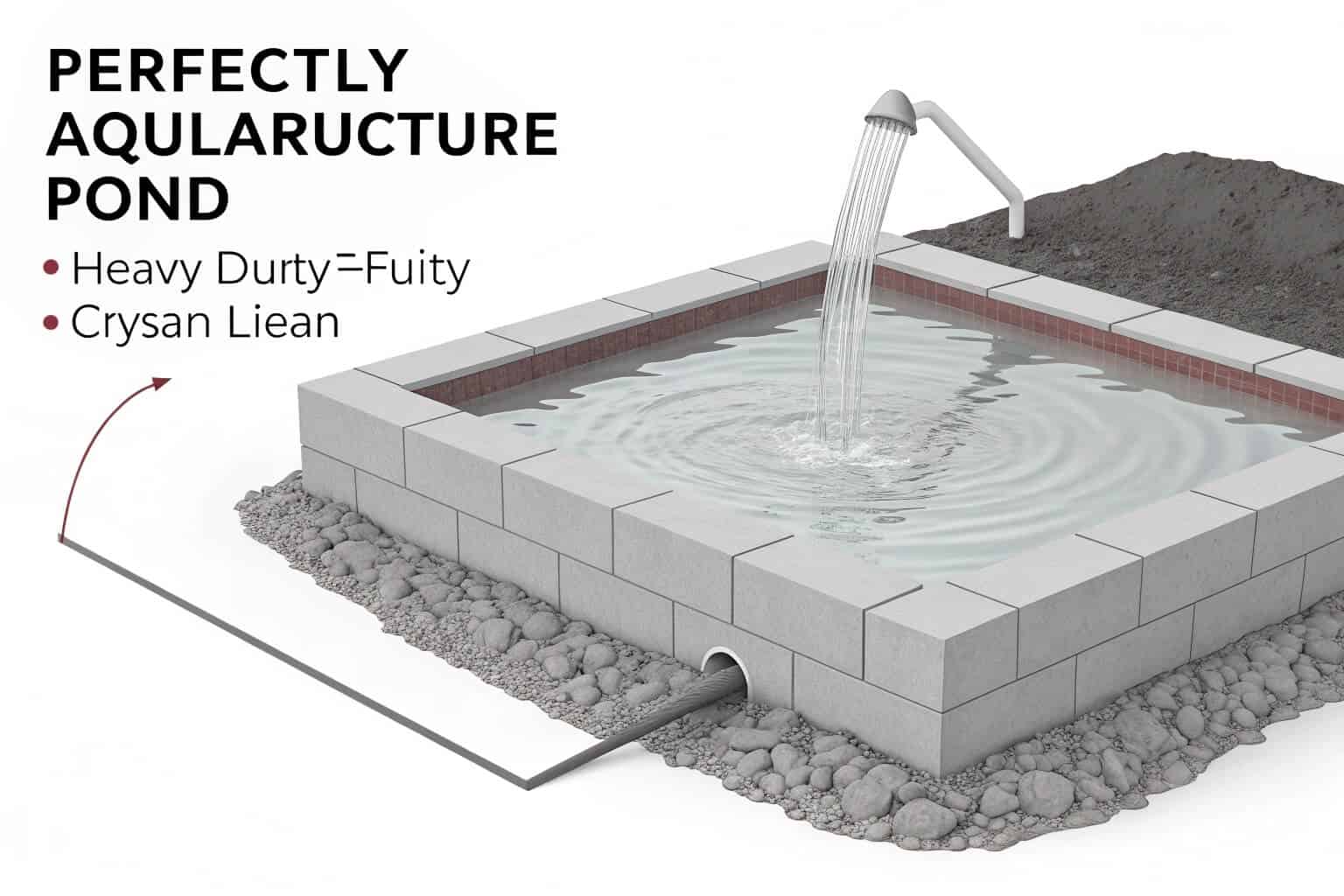
Key Design Features
A well-designed pond has specific features. It should have a manageable depth, usually between 1 to 2 meters, to ensure sunlight reaches the bottom to promote natural food growth. It also needs a gentle slope for easy harvesting. Most importantly, it must have an inlet for fresh water7 and an outlet for drainage. This allows you to control water levels and perform water exchanges to manage quality.
Earthen vs. Lined Ponds
The type of pond also defines it. Each has its place depending on your goals and resources.
| Pond Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Earthen8 | Low initial cost, feels natural, can support biodiversity. | Prone to water seepage, can be difficult to clean and dry. |
| Lined9 | Excellent water control, durable, easy to clean, prevents erosion. | Higher initial cost, can be less natural for some species. |
At Bancy, we specialize in lined solutions like collapsible tanks10 because they offer superior control and flexibility. You can set them up almost anywhere, prevent water loss, and ensure the environment is clean, which is critical for preventing diseases and managing your stock effectively.
What is a pond system?
You know the parts, but how do they work together? A pond is just one piece. Understanding the "system" is key to making it all work and become profitable.
A pond system is an integrated set of components working together to create a productive aquaculture environment. It’s not just the pond, but also the water, the animals, the feed, and the management practices. Think of it as a factory where the final product is healthy fish.
Thinking in "systems" was a game-changer for me. It’s about seeing the connections between everything instead of just focusing on individual parts. A pond system is a living cycle11, and your job as a farmer is to keep that cycle in balance. When it’s balanced, it’s incredibly productive. When it’s not, things can go wrong very quickly.
The Input-Process-Output Model
You can think of it like this:
- Inputs: You add things to the system. This includes fish stock12 (the small fish you start with), feed, and fresh water. You also input energy through sunlight and sometimes electricity for pumps or aerators. Every input has a cost, so efficiency is key.
- Process: Inside the pond, complex biological and chemical processes happen. Fish eat the feed and natural food, then grow. They produce waste, which is broken down by bacteria. Algae grows using sunlight and nutrients. Oxygen is dissolved into the water from the air and from the algae.
- Outputs: The main output you want is harvested fish. But there are other outputs, like wastewater13, which needs to be managed responsibly.
The Importance of Balance
A successful manager keeps this cycle in balance. For example, if you add too much feed (input), the water quality14 will drop (process), and you’ll end up with sick or dead fish (bad output). It’s a constant balancing act15 that requires attention and understanding.
What is in the pond raceway system?
Want to grow more fish in less space? Traditional ponds have limits on how many fish you can stock. The pond raceway system is an innovative solution that can dramatically increase your yield.
A pond raceway system, or PRS, contains channels or "raceways" built within a traditional pond. Water is continuously circulated through these raceways, bringing fresh, oxygenated water to the fish, which are concentrated in these channels. This boosts density and growth rates significantly.
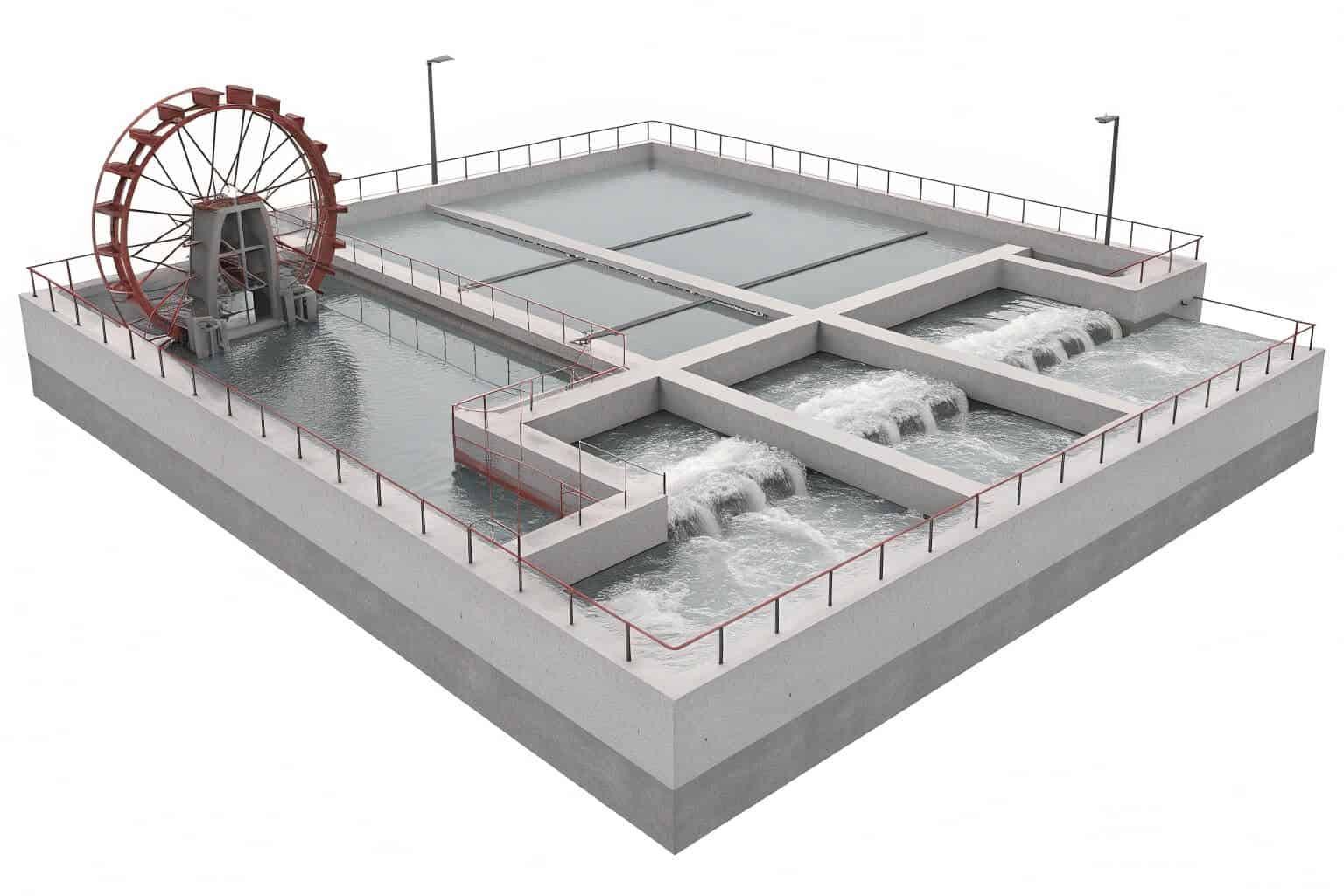
I’m particularly excited about pond raceway systems. They are a clever mix of old and new technology. You get the stability and low cost of a large pond, which acts as a natural water treatment area16, but with the high-density benefits of a modern raceway. It’s the best of both worlds.
Core Components
Here’s what you’ll find inside one:
- Raceway Channels17: These are narrow lanes, often built with concrete or liners, where the fish are kept. This concentration makes feeding, observing, and harvesting the fish much easier than in a large, open pond.
- Water Circulation18: This is the engine of the system. Air-lift pumps or paddlewheels continuously move water from the main pond area into and through the raceways. This constant flow provides a steady supply of oxygen and carries away waste.
- Waste Collection19: As water flows out of the raceway, it carries fish waste with it. This waste then settles in the larger, calmer pond area. Here, natural bacterial processes can break it down, effectively treating the water before it’s cycled back through.
Key Advantages
I’ve seen farms increase their production by 20-30% or more just by retrofitting their ponds with a raceway. It requires more active management, like monitoring flow rates and cleaning the channels, but the payoff in productivity can be huge. The main advantages are higher stocking densities20, improved feed management, and easier harvesting.
Conclusion
In the end, pond aquaculture is a powerful and accessible tool for food production. Whether you use a simple earthen pond or an advanced raceway, success comes from understanding it as a system.
- This resource will help you grasp the complexities of ecosystems in aquaculture, crucial for effective management and productivity. ↩
- Explore this link to understand how PVC-lined tanks can enhance pond management and fish health. ↩
- Learn about the importance of water circulation in ponds and its impact on fish and plant life. ↩
- Understanding aeration systems can significantly improve your pond’s health and fish yield, making it a crucial resource for pond management. ↩
- This resource will guide you on creating and sustaining a balanced pond ecosystem, crucial for successful fish farming. ↩
- Exploring best practices for growing healthy fish can help you optimize your aquaculture efforts and ensure a successful yield. ↩
- Exploring the significance of a fresh water inlet can help you maintain optimal water quality and ecosystem balance. ↩
- Explore this link to understand how earthen ponds can enhance biodiversity while weighing their challenges. ↩
- Explore this link to understand how lined ponds can enhance water management and prevent erosion. ↩
- Discover the advantages of collapsible tanks for flexibility and water conservation in your pond setup. ↩
- Exploring living cycles in ecosystems can provide insights into sustainable farming and environmental health. ↩
- Understanding fish stock is crucial for effective aquaculture management and sustainability. ↩
- Proper wastewater management is essential for environmental protection and maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems. ↩
- Understanding water quality management is crucial for healthy fish farming and can prevent costly losses. ↩
- Exploring management strategies can enhance your skills in maintaining equilibrium in aquaculture operations. ↩
- Discover the role of natural water treatment areas in enhancing sustainability and efficiency in aquaculture. ↩
- Explore this link to understand the design and benefits of raceway channels in fish farming, enhancing your aquaculture knowledge. ↩
- Understanding water circulation is crucial for maintaining healthy fish environments and optimizing aquaculture productivity. ↩
- Exploring waste collection methods can enhance your knowledge of sustainable aquaculture practices and water treatment. ↩
- This resource will explain the impact of stocking densities on fish health and farm output, crucial for maximizing production. ↩