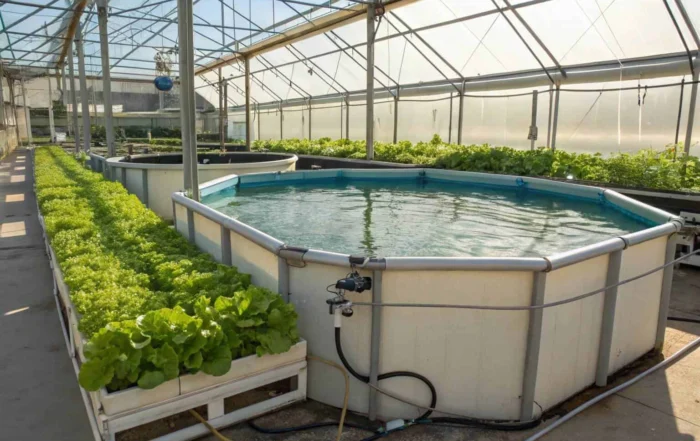
Is our growing demand for seafood pushing ocean ecosystems to the brink? Wild fish stocks are dwindling under pressure, threatening both marine life and our future food security.
The main purpose of aquaculture is to farm fish, shellfish, and other aquatic organisms in controlled settings. This provides a sustainable source of seafood, helps restore natural habitats, and drives economic growth, all while easing the pressure on wild fisheries.

As someone who has watched the aquaculture industry for years, I see it as a vital global solution. It’s about more than just farming fish; it’s a response to a critical need. I believe its purpose is threefold: producing food, restoring ecosystems, and creating economic opportunity. By cultivating species in controlled environments, we can provide a steady supply of protein to feed a growing population. At the same time, we can help rebuild threatened marine habitats and support coastal communities with new jobs. This industry is tackling some of the biggest challenges we face today.
What is the most important thing in aquaculture?
Are you thinking of starting a fish farm but worried about the risks? Many new farms fail because of problems that could have been prevented, turning a promising venture into a loss.
The most important thing in aquaculture is sustainable management. This means constant attention to water quality, proactive disease prevention, and smart feeding strategies. Good management is the key to a healthy farm and long-term success, preventing pollution and production losses.
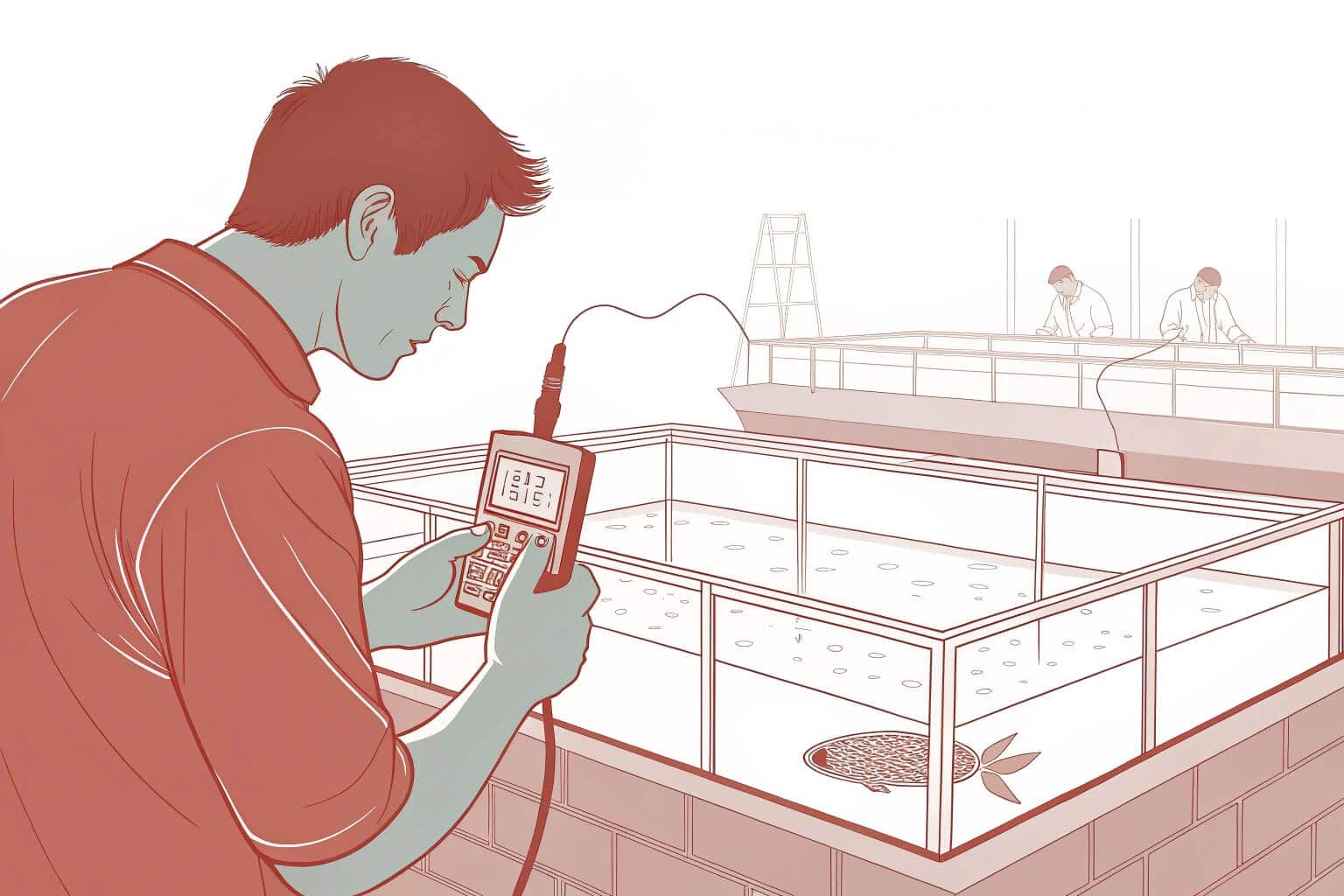
I have seen firsthand how critical sustainable management1 is. The success or failure of a farm often comes down to how well it controls its environment. Ignoring factors like water quality or disease can lead to disaster, but with the right approach, these risks can be managed. Innovations are making this easier than ever. For example, modern systems can minimize the environmental footprint while maximizing output. I believe that focusing on sustainability is not just good for the planet; it’s the smartest way to run a profitable aquaculture business. It ensures that the farm can thrive for years to come.
The Critical Role of Water Quality
Water is everything in aquaculture. I’ve visited farms where perfect water chemistry led to incredible growth rates. On the other hand, I’ve seen farms where poor water quality caused widespread disease and failure. Parameters like pH, ammonia, and oxygen levels must be monitored constantly. A small change can have a huge impact on the health of the fish. This is why reliable equipment2 and consistent testing are investments that always pay off.
Proactive Disease Prevention
Once a disease takes hold on a farm, it can be incredibly difficult and expensive to treat. The best strategy is always prevention. This starts with a clean, stable environment. It also includes sourcing healthy, disease-free juveniles and implementing biosecurity measures3 to stop pathogens from entering the system. I always advise farmers to think like doctors: prevent the illness instead of just treating the symptoms.
Innovations in Sustainability
The industry is moving towards more sustainable practices, and technology is leading the way. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) are a great example. These systems filter and reuse water, dramatically reducing the farm’s environmental impact.
| Feature | Traditional Ponds | Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS)4 |
|---|---|---|
| Water Use | High (constant exchange) | Low (up to 99% recycled) |
| Land Use | Large footprint | Compact and scalable |
| Waste Management | Discharged into environment | Collected and treated |
| Control | Limited (weather dependent) | High (fully controlled environment) |
What is the main idea of aquaculture?
Do you think of fish farming as just a simple pond with some fish in it? This view misses the science and precision that make modern aquaculture a powerful and efficient food production system.
The main idea of aquaculture is to apply the principles of agriculture to aquatic life. It is about cultivating fish, shellfish, or algae with scientific control over their environment to achieve efficient, predictable, and high-yield production, moving beyond chance-based wild harvesting.

I often explain aquaculture5 as "farming, but in water." The core concept is the same as land-based agriculture: we are creating a controlled environment6 to produce food efficiently. Instead of relying on hunting and gathering from the wild, we are taking charge of the entire life cycle. This shift from capture to cultivation allows for a much more stable and predictable supply. It also lets us optimize conditions for growth and health in a way that is impossible in the open ocean. This idea is not new, but modern technology has transformed it into a high-tech industry capable of feeding millions.
Precision and Control
The key difference between aquaculture and fishing is control. In aquaculture, we manage every variable, from the water temperature and pH to the exact amount and type of feed the fish receive. This precision allows us to create the perfect conditions for growth. I’ve worked with farmers who use automated systems to monitor their tanks 24/7. This level of control minimizes stress on the fish, improves feed conversion rates, and leads to a healthier, more uniform product. It turns farming into a science.
From Hunting to Farming
Humanity made a huge leap forward when we shifted from hunting wild animals to raising livestock. Aquaculture represents the same transition for seafood. For centuries, we have been hunters of the sea. Now, we are becoming farmers. This change is essential for sustainability. Wild fisheries have limits, and many are already over-exploited. By farming fish, we can meet growing demand without emptying our oceans. It’s a fundamental change in our relationship with the aquatic world.
| Aspect | Wild-Capture Fishing7 | Aquaculture |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Wild populations | Farm-raised stock |
| Control8 | Low (subject to nature) | High (managed environment) |
| Yield9 | Unpredictable | Stable and predictable |
| Sustainability10 | Risk of overfishing | Can be highly sustainable |
What is a benefit of aquaculture?
Are you looking for healthy, sustainable food choices? The environmental cost of many protein sources is a growing concern, leaving many of us searching for better alternatives for our diet and the planet.
A major benefit of aquaculture is that it provides a nutritious, low-fat protein source with a smaller environmental footprint. It helps protect marine biodiversity by relieving the heavy pressure on wild-caught fish, giving ocean ecosystems a chance to recover.

One of the things I appreciate most about aquaculture is its dual benefit for people and the planet. On one hand, farmed fish like salmon and tilapia are packed with protein and healthy omega-3 fatty acids, making them a great choice for a healthy diet. On the other hand, producing this protein through farming has a much lower impact than many other forms of animal agriculture. It requires less land and fresh water, and it helps us leave more fish in the sea. When I see a client successfully harvesting fish from a sustainable farm11, I know we are creating a food source that is good for us and for future generations.
A Healthier Protein Choice
Farmed fish are an excellent source of lean protein, which is essential for building muscle and maintaining a healthy body. Many species are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids12, which are known to support heart and brain health. In a world where many diets are heavy in unhealthy fats, aquaculture provides a delicious and nutritious alternative. It’s a simple switch that can have a big impact on personal well-being.
Protecting Our Oceans
The world’s oceans are in trouble. Decades of industrial fishing have depleted many fish populations. Aquaculture offers a direct solution to this problem. Every farmed fish that reaches a dinner plate is one less fish that needs to be pulled from the ocean. This gives wild stocks a chance to rebound and helps restore the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. By choosing farmed seafood13, consumers can play a role in ocean conservation.
Lower Environmental Footprint
When we compare different ways of producing animal protein, aquaculture often comes out on top. It is generally more efficient in converting feed into protein than land animals. The table below shows a simplified comparison.
| Protein Source | Feed Conversion Ratio14 (Approx.) | Carbon Footprint |
|---|---|---|
| Farmed Salmon | 1.2 : 1 | Low |
| Chicken | 2 : 1 | Medium |
| Pork | 3 : 1 | Medium-High |
| Beef | 6 : 1 | High |
What are three things aquaculture is used for?
Do you believe aquaculture’s only purpose is to grow fish for supermarkets? This common idea overlooks the diverse and vital roles this industry plays in our environment, economy, and even our entertainment.
Aquaculture has three primary uses: first, large-scale commercial food production for global markets; second, ecological restoration to rebuild habitats and replenish wild species; and third, specialized applications in research, education, and recreation, such as in labs or sport-fishing ponds.

I find the versatility of aquaculture fascinating. While its role in food production is the most visible, its impact goes much further. I’ve supplied our Bancy tanks to commercial farms that feed thousands, but I’ve also worked with conservation groups using them to breed endangered fish for release into the wild. The same basic technology can be adapted for so many different goals. This flexibility is one of the industry’s greatest strengths. From feeding cities to healing rivers, aquaculture is a tool with many important jobs, and its potential is still growing.
Feeding the World
The most significant use of aquaculture is commercial food production. Farms around the world raise huge quantities of salmon, shrimp, tilapia, and oysters to supply restaurants and grocery stores. This is a massive global industry that provides a reliable and affordable source of protein for billions of people. As the world population grows, the importance of this role will only increase. Our durable, customizable fish tanks15 are designed to support these large-scale operations, ensuring they can operate efficiently and safely.
Healing Ecosystems
Aquaculture is a powerful tool for environmental conservation. Scientists and conservation groups use it to breed species that are threatened or endangered in the wild. These farm-raised animals are then released to help rebuild wild populations16. This is being done with fish, but also with other species like oysters, which are crucial for filtering water and creating reef habitats. In this way, farming can help undo some of the damage that has been done to our aquatic ecosystems.
Beyond the Dinner Plate
The applications of aquaculture extend into many other fields. In science, researchers use fish as model organisms17 to study genetics, disease, and toxicology. Public aquariums use aquaculture techniques to maintain their exhibits and educate millions of visitors about marine life. There is also a recreational side to the industry. Many private ponds and lakes are stocked with farm-raised fish for sport fishing, creating leisure opportunities and supporting local tourism economies.
Conclusion
In short, aquaculture is a dynamic and essential industry. It is a key to providing sustainable food, restoring our planet’s ecosystems, and driving economic growth for communities around the world.
- Explore this link to discover effective strategies that can enhance sustainability and profitability in farming. ↩
- Reliable equipment is essential for maintaining water quality, preventing disease, and ensuring the sustainability of aquaculture operations. ↩
- Understanding biosecurity measures is crucial for preventing disease outbreaks on farms, ensuring a healthy environment for livestock. ↩
- Explore this resource to understand how RAS technology reduces environmental impact and improves aquaculture efficiency. ↩
- Explore this link to understand how modern innovations are transforming aquaculture into a high-tech industry capable of feeding millions. ↩
- Learn how creating controlled environments enhances efficiency and sustainability in food cultivation, similar to aquaculture. ↩
- Explore this link to understand the ecological effects and sustainability challenges of wild-capture fishing. ↩
- Understanding control levels helps evaluate sustainability and management practices in seafood production. ↩
- Explore this resource to understand how yield stability varies between wild and farmed seafood, aiding sustainable choices. ↩
- Explore this resource to understand how aquaculture can be a sustainable alternative to wild-capture fishing. ↩
- Explore this link to learn effective strategies for sustainable aquaculture that benefit both the environment and food security. ↩
- Learn about the importance of omega-3 fatty acids and how they contribute to overall well-being and disease prevention. ↩
- Discover how choosing farmed seafood can help reduce pressure on wild fish populations and support marine ecosystems. ↩
- Understanding Feed Conversion Ratio helps evaluate the efficiency of different animal protein sources, making it essential for sustainable food production. ↩
- Discover expert tips and product options to optimize your aquaculture setup for better productivity and safety. ↩
- Discover how aquaculture contributes to conservation efforts by restoring endangered aquatic species in their natural habitats. ↩
- Explore this link to understand how fish contribute to genetics, disease, and toxicology studies, advancing scientific knowledge. ↩







