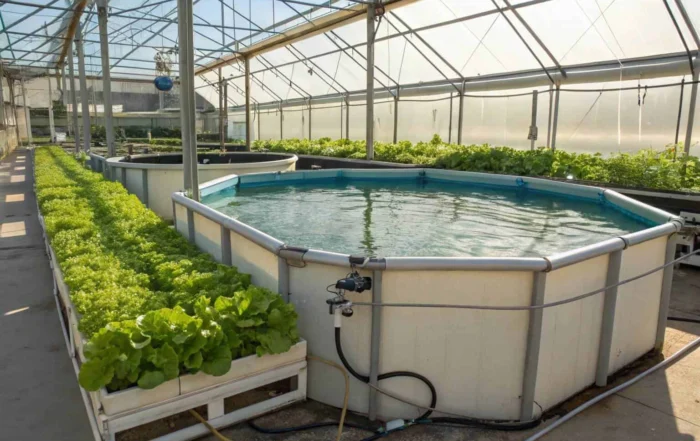
Struggling to find a sustainable protein source? You’re not alone. The demand for fish is soaring, but traditional fishing can’t keep up. What if there’s a simpler way?
Tilapia is often considered the easiest fish to farm, especially for beginners. They are hardy, grow fast in warm climates, and have a flexible diet. This makes them a low-risk, high-reward choice for starting your own aquaculture project.

But "easiest" doesn’t always mean "best" for everyone. Your goals, climate, and resources all play a part. Let’s explore which fish might be the perfect fit for you.
Which fish are easiest to farm?
Want to start fish farming but feel overwhelmed by the options? Choosing the right species is crucial for success. Don’t let complexity stop you from this profitable venture.
Besides Tilapia, other easy-to-farm fish include Catfish and Carp. Catfish are incredibly resilient and can tolerate poor water conditions. Carp are also very hardy and can adapt to various environments, making them great for beginners.

I’ve seen many first-timers succeed with Tilapia. Their rapid growth means you can see a return on your investment in as little as six months. They are also omnivores, which helps keep feed costs down. I remember a client in Southeast Asia who started with a small backyard pond and was able to supply his local market within a year. Catfish are true survivors. They can breathe air, which allows them to thrive in water with low oxygen levels. This resilience makes them a forgiving choice for those still learning about water quality management1. Their mild flavor also gives them broad market appeal. To help you decide, here’s a simple comparison:
Key Considerations for Beginners
For those just starting, focusing on the basics is essential. Water quality2 is paramount; regular testing for ammonia, nitrites, and pH levels will prevent most common problems. Feeding is another critical area. While species like Tilapia are not picky, providing a balanced diet ensures faster growth and better health. Finally, your initial setup doesn’t have to be complicated. I’ve seen many successful small-scale farms begin with simple, cost-effective equipment like our collapsible fish tanks3. They are easy to set up, durable, and perfect for a backyard operation, allowing you to get started without a massive initial investment.
Comparing Easy-to-Farm Fish
| Feature | Tilapia | Catfish | Carp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate4 | Fast (6-8 months) | Moderate (8-12 months) | Moderate (12-18 months) |
| Hardiness | High | Very High | High |
| Diet | Omnivore | Omnivore/Carnivore | Omnivore |
| Market Demand5 | High | High | Moderate |
Which fish farming is most profitable?
Are you looking to turn your farming hobby into a real business? Profitability is key. Some fish can generate significantly more income than others, but it comes with its own challenges.
Catfish farming is often the most profitable, especially in regions like Africa and Asia, due to its high demand and resilience. However, high-value species like Salmon or Trout can yield greater profits if you have the right setup and expertise.
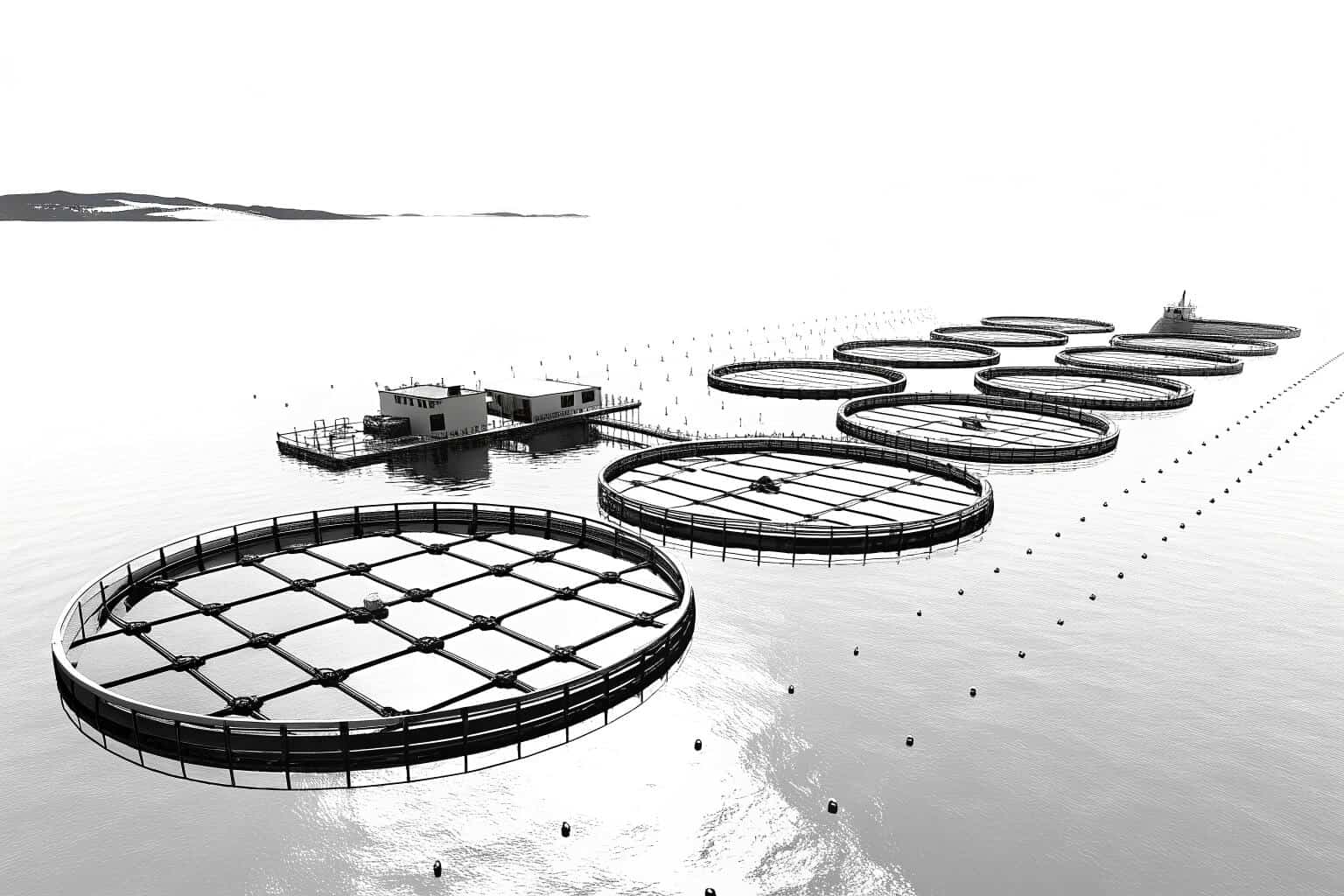

From my experience, the stability of the catfish market makes it a reliable money-maker. They have a consistent demand and can be farmed at high densities, maximizing your output per square meter. A key advantage is their tolerance for different conditions, which lowers the risk of losing stock. Farming salmonids is a different ball game. It requires significant upfront investment in cooling systems and high-quality feed. However, the market price for salmon is much higher. I worked with a farm in Europe that successfully implemented a recirculating aquaculture system (RAS)6 for trout, and their profits were impressive, but it took a lot of technical skill. Don’t overlook niche species like shrimp or eels. While they can be more susceptible to disease, they command premium prices. Success here depends on finding the right buyers and maintaining pristine water conditions. It’s a specialized field but can be very lucrative.
Managing Costs for Higher Profits
Profit in aquaculture isn’t just about the sale price; it’s about managing your expenses. Feed is the largest operational cost, often accounting for over 60% of the total budget. Optimizing feeding schedules7 and using high-quality, appropriate feed can significantly reduce waste and improve conversion ratios, directly boosting your bottom line. Energy costs for pumping, aeration, and heating or cooling are another major expense. Investing in energy-efficient equipment8 or integrating sustainable solutions like solar power can lead to substantial savings. I’ve also seen farmers partner with local producers to source cheaper feed ingredients or use integrated systems, like aquaponics, to create additional revenue streams from the same resources.
Profitability at a Glance
| Fish | Profit Potential | Key Success Factors | Target Market |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catfish | High | High-density farming9, stable market | Broad (Local & Export) |
| Salmon/Trout | Very High | Advanced tech, cold water systems10 | High-end Restaurants, Retail |
| Shrimp/Eel | High | Disease management, niche buyers | Specialty & Export Markets |
What is the easiest fish to breed and make money?
Want to control your entire production line from start to finish? Breeding your own fish can cut costs and increase profits. But not all fish are easy to breed in captivity.
Tilapia are one of the easiest fish to breed and monetize. They reproduce quickly and easily in ponds or tanks with minimal intervention. This allows you to create a self-sustaining population and sell fingerlings to other farmers for extra income.

I’ve seen tilapia populations11 explode in a matter of months. A single female can produce hundreds of fry. The key is to manage the population to prevent overcrowding, which can stunt growth. Separating the males and females or introducing a predator fish can help control numbers. Catfish are also relatively easy to breed, though it might require a bit more effort than tilapia. You may need to induce spawning using hormones. Once you master the technique, you can produce a steady supply of fingerlings. This is a great way to diversify your income streams.
From Breeding to Market
Successfully breeding fish is only half the battle; you also need a plan to raise and sell them. Once your fingerlings hatch, they require a specific environment to thrive. This often means a separate, smaller tank with carefully controlled water parameters and specialized fry feed. As they grow, you’ll need to move them to larger grow-out tanks. This is where having a flexible setup, like our customizable collapsible ponds12, becomes a huge advantage. You can easily create different zones for different growth stages. Finally, having a market for your fish13 is crucial. You can sell them as fingerlings to other farmers or raise them to market size yourself. Building relationships with local restaurants, markets, or even other farms early on will ensure you have buyers ready when your fish are.
Breeding Comparison
| Fish | Breeding Ease | Spawning Method14 | Fry Care | Profit Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tilapia | Very Easy | Natural Spawning | Minimal | High |
| Catfish15 | Moderate | Induced Spawning | Moderate | High |
| Carp | Moderate | Natural/Induced | Moderate | Moderate |
Which fish is the best for farming?
With so many factors to consider, how do you choose the "best" fish? The answer isn’t one-size-fits-all. It depends entirely on your specific situation and goals.
The "best" fish for farming depends on your climate, resources, and market. For warm climates and beginners, Tilapia is often best. For those focused on profit and resilience, Catfish is a strong choice. For high-end markets, Salmon or Trout are ideal.
Your local climate is a huge factor. Tilapia and catfish thrive in warm water16, while trout and salmon need cold, clean water. Trying to farm a fish outside its ideal temperature range will lead to high energy costs and stressed, unhealthy fish. I always advise clients to start by researching what grows well locally. Think about your available space, water, and capital. A small backyard setup is perfect for a collapsible fish pond with tilapia. A larger operation with more capital might consider a more complex system for a higher-value species. Remember that feed can be up to 60% of your costs, so factor that into your budget. Who are you selling to? Research your local market to see what fish are in demand and what prices they fetch. Sometimes a less common fish can be more profitable if you have a ready market for it. Connecting with local restaurants or markets before you start is a smart move.
The Role of Technology in Modern Farming
Technology is transforming aquaculture, making it more efficient and sustainable. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS)17 are a prime example. These closed-loop systems filter and reuse water, drastically reducing water consumption and allowing for farming in areas with limited water resources. While the initial investment can be high, the long-term savings on water and the ability to control the environment precisely can lead to higher yields and healthier fish. On a smaller scale, innovations in equipment are making farming more accessible. Our durable, collapsible fish tanks, for instance, offer a flexible and affordable alternative to traditional ponds. The use of automated feeders and water quality sensors18 can also save time and prevent costly mistakes, making the entire operation run more smoothly.
Decision-Making Framework
| Factor | Questions to Ask Yourself | Recommended Fish (Examples)19 |
|---|---|---|
| Climate | Is my climate warm, temperate, or cold? | Warm: Tilapia, Catfish; Cold: Trout, Salmon |
| Resources | What is my budget? How much space do I have? | Low Budget/Small Space: Tilapia; High Budget/Large Space: Salmon |
| Market20 | What is popular locally? Can I access high-end markets? | Local Market: Catfish, Carp; High-End: Trout, Shrimp |
Conclusion
Choosing the right fish is the first step to a successful aquaculture venture. By matching the species to your climate, resources, and market, you can build a profitable business.
- Effective water quality management is crucial for healthy fish; explore this link to learn best practices and ensure your fish thrive. ↩
- Understanding water quality is crucial for fish health; explore this link to learn effective management techniques. ↩
- Discover how collapsible fish tanks can simplify your setup and enhance your backyard farming experience. ↩
- Understanding growth rates helps in selecting the right fish for aquaculture and maximizing yield. ↩
- Exploring market demand can guide investment decisions and ensure profitability in fish farming. ↩
- Explore this resource to understand how RAS can boost profitability and sustainability in trout aquaculture. ↩
- Discover effective strategies to reduce waste and increase efficiency in aquaculture by exploring optimized feeding schedules. ↩
- Learn how energy-efficient equipment can significantly cut costs and promote sustainability in aquaculture operations. ↩
- Explore this resource to learn effective techniques for maximizing fish farm productivity through high-density farming. ↩
- Discover how innovative technology and cold water systems can enhance the success of salmon and trout aquaculture. ↩
- Explore effective strategies to manage tilapia populations and prevent overcrowding, ensuring healthy growth. ↩
- Explore this resource to learn how flexible pond setups can optimize your fish farming process and adapt to different growth stages. ↩
- Discover effective strategies to connect with local markets, restaurants, and other buyers to ensure a successful fish selling business. ↩
- Discover various spawning methods to optimize fish reproduction and increase your farm’s productivity. ↩
- Explore this resource to learn effective breeding, spawning, and fry care techniques for catfish, maximizing profit potential. ↩
- Explore this link to learn about suitable warm water fish like tilapia and catfish, which are ideal for your local climate and easy to farm. ↩
- Explore this resource to understand how RAS can improve sustainability and efficiency in aquaculture. ↩
- Learn how automation technology can enhance fish farming productivity and health. ↩
- Explore this resource to find suitable fish options based on your climate, ensuring successful aquaculture. ↩
- Learn how to select the right fish species to meet market demands and maximize profitability. ↩







