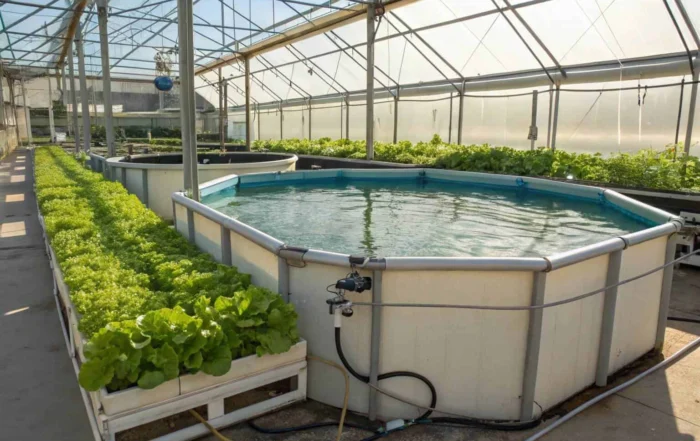
Struggling with water usage and environmental impact in your fish farm? These challenges can limit your growth and profitability. RAS offers a revolutionary, sustainable solution for modern aquaculture.
RAS is a technology that reuses water in fish farming. It filters and purifies water from fish tanks, allowing it to be recirculated. This creates a controlled, high-density environment, boosting fish health and growth while conserving water and minimizing environmental impact.
It sounds like a game-changer, right? As someone deep in this industry, I know you have more specific questions. You’re probably wondering what it really means for your daily operations, what the acronym stands for, and what the potential downsides are. Let’s break it down further.
What is RAS for fish?
Worried about water quality and disease outbreaks in your tanks? Poor conditions can wipe out your stock overnight. RAS provides a clean, stable, and controlled environment for your fish.
For fish, RAS means living in a highly controlled and clean environment. The system continuously filters out waste and re-oxygenates the water. This reduces stress, minimizes disease risk, and provides optimal conditions for faster growth and better health, leading to a higher quality product.

As a farmer, I see my fish as my most valuable asset. Their well-being directly translates to my bottom line. In traditional ponds, I was always fighting against nature—unpredictable weather, algae blooms, and hidden pathogens. With RAS1, I feel more like a conductor of an orchestra than a firefighter. I am in control. The system creates a perfect world for the fish. Think of it as a five-star, all-inclusive resort. The water is always clean, the oxygen is plentiful, and the temperature is just right. This stability is something you can’t guarantee in an outdoor pond. Fish in a stable environment2 are less stressed, and less-stressed fish eat better, grow faster, and are far more resistant to disease. This means I can raise more fish in a smaller space, and the final product is consistently high-quality, which my customers appreciate.
How RAS Creates the Ideal Environment
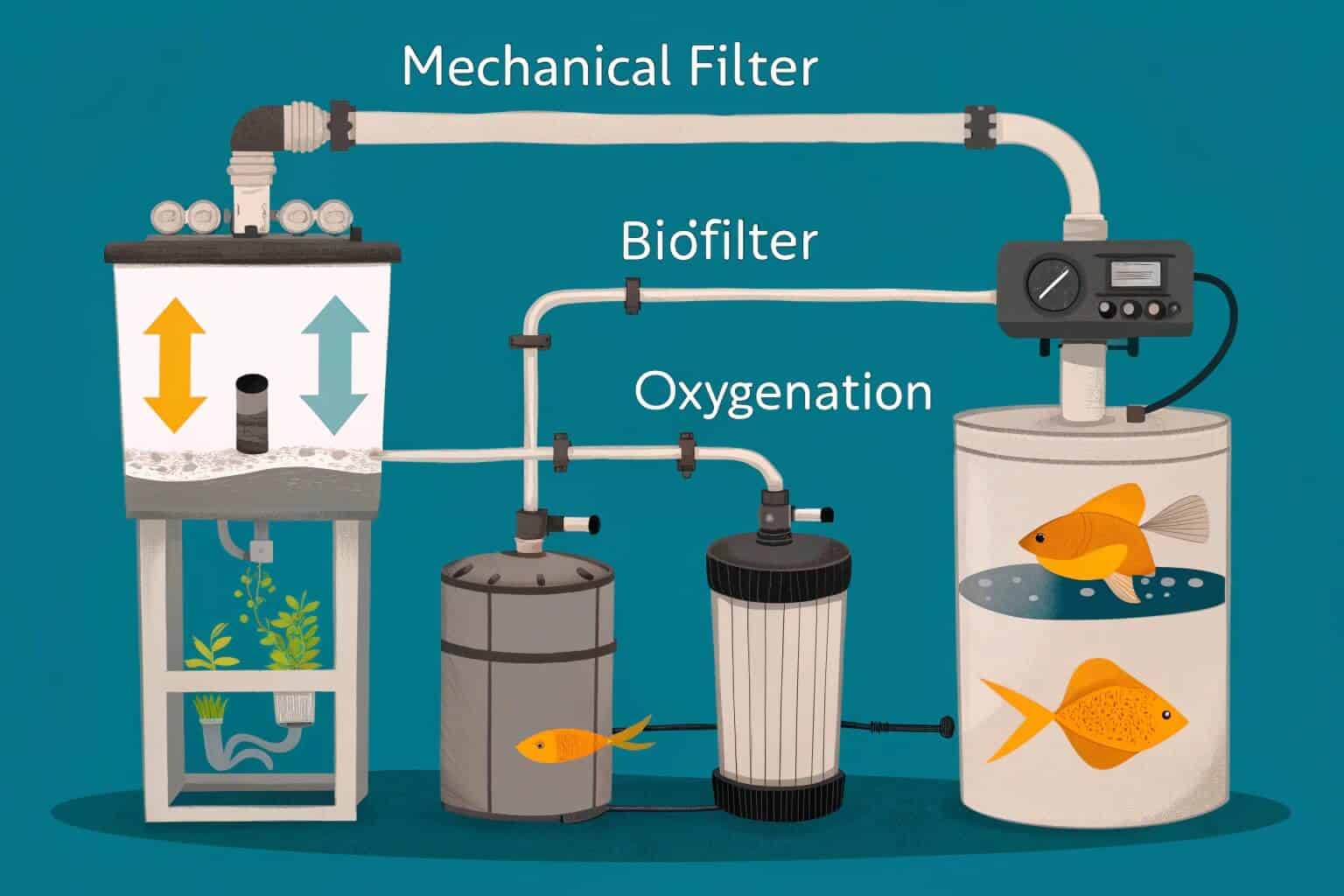
The magic of RAS lies in its components. A mechanical filter first removes the solid waste, like feces and uneaten feed. Then, a biological filter, the heart of the system, uses beneficial bacteria to convert toxic ammonia from fish waste into much safer nitrates. Some systems add protein skimmers to remove dissolved organic compounds, and UV sterilizers3 to kill any free-floating bacteria or viruses. Finally, an oxygenator ensures the water returning to the tank is rich in dissolved oxygen. It’s a complete life-support system.
A Comparison with Traditional Ponds
To really understand the difference, let’s look at a direct comparison. I’ve managed both types of farms, and the contrast is stark.
| Feature | Traditional Pond | Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Quality | Variable, affected by weather and runoff | Stable and controlled |
| Stocking Density4 | Low | Very High |
| Disease Risk5 | High, difficult to control | Low, easier to manage and prevent |
| Water Usage | High, constant replacement needed | Very Low, over 90% is recycled |
| Growth Rate | Slower, seasonal | Faster, year-round production |
What does RAS stand for in agriculture?
Hearing technical acronyms can be confusing. Not knowing the terms makes it hard to evaluate new tech. RAS simply stands for Recirculating Aquaculture System, a key innovation in modern farming.
In agriculture, RAS stands for Recirculating Aquaculture System. It’s a method of farming aquatic organisms like fish, shrimp, or plants by reusing water. This closed-loop approach is a major step forward in sustainable agriculture, especially in areas where water is scarce.
When I first heard the term, it sounded complicated. But once I broke it down, it made perfect sense. It’s not just a product; it’s a philosophy of farming. It’s about being smart with our resources and creating the best possible conditions for our stock. In my experience, understanding the name is the first step to understanding the power of the technology. It represents a shift from simply using resources to actively managing them. This concept is crucial not just for fish farming but for the future of all agriculture. As we face global challenges like water scarcity6 and the need for more food, systems like RAS are not just an option; they are becoming a necessity. It’s about producing more with less, a principle that resonates deeply with me as a business owner and a steward of the environment.
Breaking Down “Recirculating”
The "Recirculating7" part is the core concept. In a traditional farm, you constantly pump fresh water in and discharge wastewater out. In RAS, the water goes on a continuous loop. It flows from the fish tank, through a series of filters to get cleaned, and then it’s pumped right back into the tank. This process is incredibly efficient. We only need to replace a small fraction of the water each day, maybe 5-10%, just to account for evaporation and waste removal. This is a massive saving compared to flow-through systems.
Why It’s a “System”
This is not just a single piece of equipment you buy off a shelf. It’s an integrated "System" where every part has a critical job. The tanks, pumps, filters, and monitoring equipment must all work together seamlessly. This is why proper design and management are so important. It’s a technological approach to farming.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Fish Tank | Houses the aquatic life in a controlled space. |
| Mechanical Filter8 | Captures and removes solid waste particles. |
| Biological Filter9 | Converts toxic ammonia into less harmful nitrates. |
| Pump | The heart of the system, ensuring constant water circulation. |
| Oxygenator10 | Adds essential dissolved oxygen back into the water. |
What are the disadvantages of the RAS?
Is RAS sounding too good to be true? You’re right to be skeptical about the potential downsides. Every technology has its challenges, and it’s crucial to understand them before investing.
The main disadvantages of RAS are the high initial investment costs for equipment and setup, and its operational complexity. It requires skilled management to maintain water quality and system functions. A power failure or system malfunction can be catastrophic without proper backup and alarm systems.

I won’t sugarcoat it; my first RAS setup was a huge financial commitment. The price tag for the tanks, industrial-grade pumps, advanced filtration units, and backup generators was daunting. There were moments I questioned if I was making the right choice. It’s not like digging a pond. This is a serious piece of industrial engineering. Furthermore, the learning curve was steep. I had to become a part-time water chemist and system engineer. You are managing a life-support system for thousands of animals in a high-density environment. A small mistake in calibration or a brief power outage can have devastating consequences. I learned the hard way that you absolutely cannot cut corners on backup systems and alarms11. It’s an investment in insurance for your entire stock.
The Financial Hurdle: Initial Costs
The upfront capital12 is the biggest barrier for most people. You’re not just buying tanks; you’re investing in a sophisticated facility. This includes biological and mechanical filters, powerful pumps, UV sterilizers, oxygenation systems, and, critically, a robust backup power supply. While you save on water and land costs over time, the initial outlay can be several times that of a traditional farm of a similar production capacity. This is a significant financial risk that requires careful planning and access to capital.
Operational Risks and How to Manage Them
In a high-density RAS, you’re always on the edge. Here are the main risks I’ve learned to manage:
| Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Power Outage13 | A must-have backup generator that kicks in automatically. An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) for critical sensors and alarms is also wise. |
| Pump Failure | Install redundant pumps. If one fails, the other takes over. Keep spare parts on hand and perform regular maintenance checks. |
| Disease Outbreak14 | Implement strict biosecurity protocols. Quarantine all new fish before introducing them to the main system. A good UV sterilizer is your best friend. |
| Water Quality Crash15 | Use automated sensors that continuously monitor pH, ammonia, and oxygen. These should be linked to an alarm system that alerts you on your phone, 24/7. |
What is the best fish for RAS?
Choosing the right fish is key to success. Not all species thrive in high-density environments. Picking the wrong one can lead to poor growth, stress, and financial loss.
The best fish for RAS are typically hardy, fast-growing species that tolerate high densities well. Tilapia, Barramundi, and Atlantic Salmon are popular choices. These species are resilient to minor fluctuations in water quality and have strong market demand, making them profitable for RAS farmers.
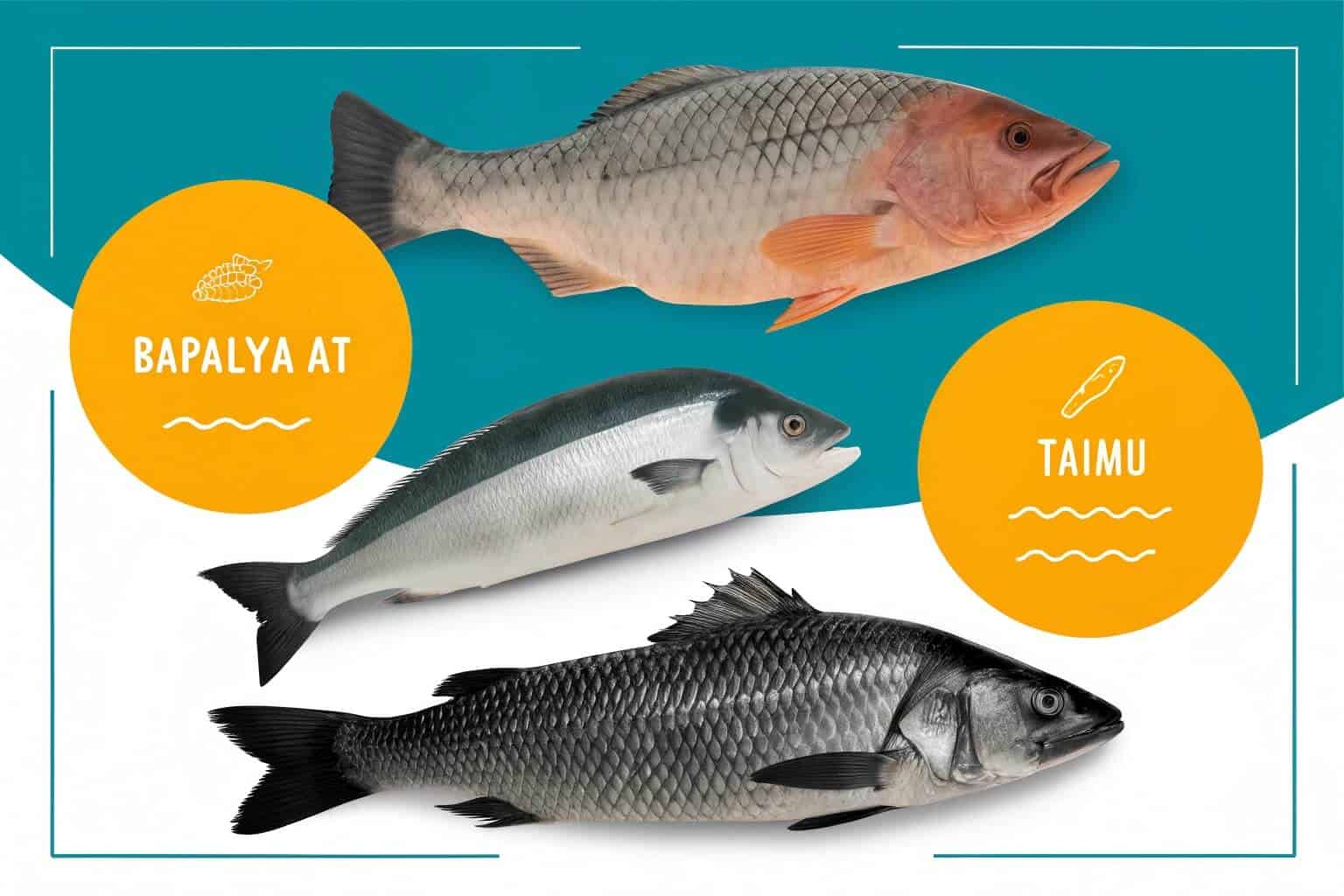

My journey with RAS involved a lot of research into this very question. I started with Tilapia because they are incredibly tough. They are forgiving, which is what you need when you are learning a new, complex system. They grow fast and handle crowding well. As my expertise grew, I looked into higher-value species16. The choice of fish really depends on your business model, your climate, and your technical skill. You have to match the species to the system and the market. For example, raising salmon17 is very profitable, but it requires expensive water-chilling equipment and precise control, making it a high-stakes, high-reward venture. It’s a balance between what the system can support and what your customers want to buy.
Key Traits of a Good RAS Candidate
When I evaluate a new species for my RAS, I look for a few key things. First, it must tolerate crowding. Second, it needs a good feed conversion ratio18, meaning it efficiently turns feed into body mass. Rapid growth is also crucial to ensure a quick return on investment. Finally, it should have a strong market price to justify the high operational costs of the system. A fish that ticks all these boxes is a strong candidate for a profitable RAS operation.
Top Species Breakdown
Here’s a quick look at some of the most popular choices based on my experience and research:
| Species | Growth Rate | Density Tolerance | Market Value | Key Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tilapia | Fast | Very High | Moderate | Sensitive to cold water. |
| Barramundi19 | Fast | High | High | Can be cannibalistic if not sorted by size. |
| Atlantic Salmon20 | Moderate | Moderate | Very High | Requires cold, pristine water and high oxygen. |
| Rainbow Trout | Moderate | High | High | Needs very high oxygen levels to thrive. |
Conclusion
In short, RAS is a powerful, sustainable fish farming method. While it has high startup costs and complexity, its benefits in water conservation, control, and yield are undeniable for modern aquaculture.
- Explore this link to understand how RAS can revolutionize fish farming and improve your yields. ↩
- Learn why a stable environment is crucial for fish well-being and how it impacts your farming success. ↩
- Discover how UV sterilizers can improve water quality and fish health by eliminating harmful pathogens. ↩
- Exploring stocking density can help optimize fish production and resource management in aquaculture. ↩
- Learning about disease risks can inform better management practices and improve fish survival rates. ↩
- This resource will provide insights into the challenges of water scarcity and innovative solutions for sustainable agriculture. ↩
- Explore this link to understand how RAS revolutionizes fish farming with water efficiency and sustainability. ↩
- Learn how a Mechanical Filter operates to keep your fish tank clean and healthy. ↩
- Understanding the Biological Filter’s function is crucial for maintaining a healthy aquarium environment. ↩
- Discover the significance of an Oxygenator in ensuring your aquatic life thrives with adequate oxygen levels. ↩
- Learning about backup systems can help ensure the safety and reliability of your aquatic life support systems. ↩
- Understanding the challenges of upfront capital can help you navigate financial risks in aquaculture investments effectively. ↩
- Explore this link to find reliable backup generators that ensure your systems stay operational during power outages. ↩
- Learn about essential biosecurity measures to prevent disease outbreaks in aquaculture, ensuring the health of your fish. ↩
- Discover advanced monitoring solutions for maintaining optimal water quality in aquaculture, crucial for fish health. ↩
- Discover various higher-value fish species that can enhance profitability in aquaculture, tailored to different markets. ↩
- Learn about the complexities and rewards of salmon farming, including the necessary equipment and market demand. ↩
- Understanding feed conversion ratio is essential for optimizing growth and profitability in aquaculture systems. Explore this link to learn more. ↩
- Learn about effective Barramundi farming techniques to maximize growth and market value while managing challenges. ↩
- Discover the essential conditions for Atlantic Salmon farming to ensure high market value and sustainability. ↩