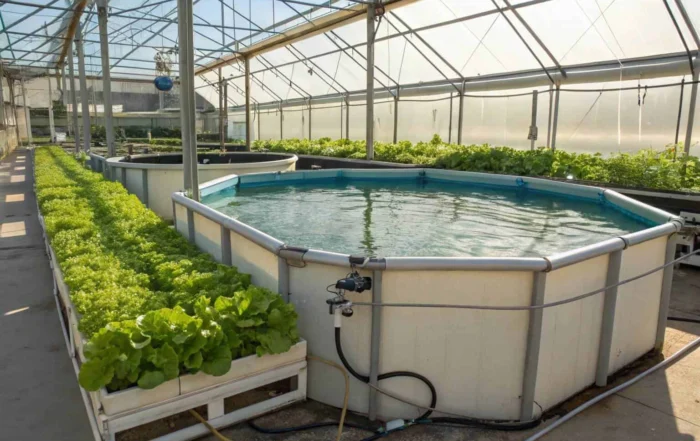
Are you an aquaculture enthusiast looking to expand your horizons? You might be wondering if it’s possible to raise saltwater fish away from the coast. It’s a challenge, but the answer is yes.
Yes, you can farm sea fish by adding salt to a pond. The key is to use a controlled environment, like a high-quality collapsible tank, to precisely manage the water’s salinity and quality. This ensures the fish not only survive but thrive far from their natural ocean habitat.

As someone deeply involved in the liquid packaging industry with my company, Bancy, I’ve seen firsthand how innovation is changing what’s possible. The growing demand for seafood is pushing us to find new, sustainable methods. Farming sea fish inland is one of the most exciting frontiers. It opens up opportunities for aquaculturists everywhere, but it requires the right tools and knowledge. Let’s explore how you can make this happen.
Can salt water fish be farmed?
Thinking about farming saltwater fish might seem complex and reserved for coastal operations. But what if you could set up a flexible, efficient system anywhere? It’s more accessible than you think.
Absolutely. Saltwater fish can be farmed in controlled environments like specialized tanks. The main task is to recreate their natural habitat by carefully managing salinity, temperature, and water quality. This makes it entirely feasible to raise them, even hundreds of miles from the ocean.
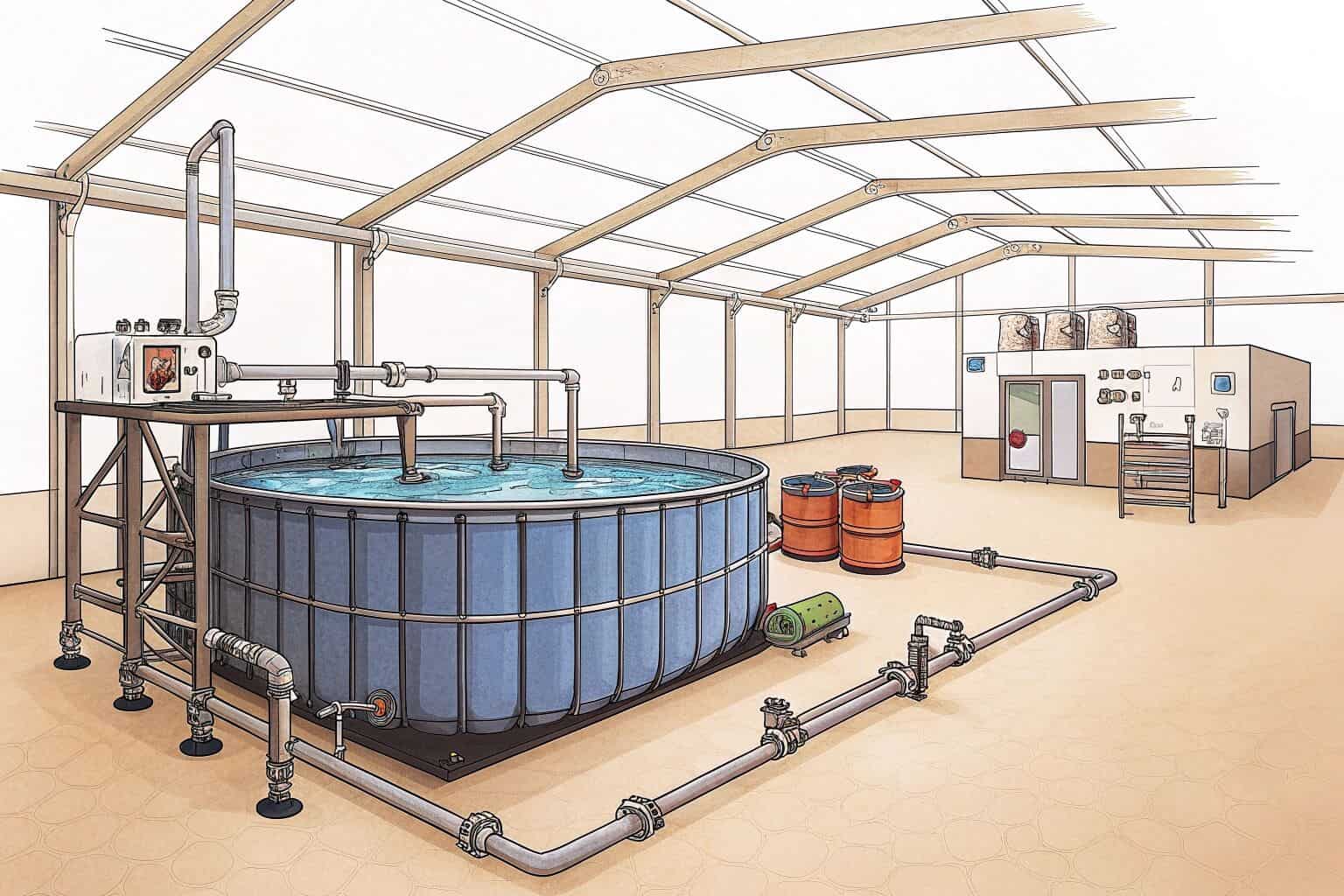

Building on this innovation, breakthroughs in water treatment and recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) have paved the way for successful inland saltwater farming. These technologies minimize water usage and waste, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional methods. So, the dream of cultivating marine life far from the shore is now a tangible reality.
The Basics of Saltwater Aquaculture
From my experience at Bancy, I’ve worked with many professionals entering this field. The core idea of saltwater aquaculture1 is simple: create a small piece of the ocean wherever you are. This means you are in complete control of the ecosystem. Unlike traditional farming, you are not just a caretaker but the creator of the environment. You decide the salt level, the pH, and the temperature. This level of control allows for optimization that is impossible in the wild. For example, you can protect your fish from natural predators and diseases, leading to higher survival rates. It also means you can grow species that are in high demand but are overfished in the ocean, contributing to both your business’s success and marine conservation. It’s a proactive approach to farming that I find truly inspiring.
Key Environmental Factors to Control
Success in this area comes down to details. The three most critical factors are salinity, temperature, and water quality2. Salinity, or the salt content, must be stable and matched to the specific species you are raising. Temperature is also crucial, as saltwater fish are often sensitive to fluctuations. You’ll need a reliable heating or cooling system. Finally, water quality is non-negotiable. This involves managing ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels through effective filtration. At Bancy, we emphasize the importance of a sealed system. Our collapsible tanks, with their double-welded seams, ensure there are no leaks, which is vital for maintaining these precise conditions without losing expensive salted water or harming the surrounding environment. It’s a closed-loop system that offers predictability and peace of mind.
Common Species for Inland Farming
So, what kind of fish can you raise? The options are exciting. Many high-value species adapt well to tank-based farming. Think of fish like Barramundi (Asian Sea Bass)3, which is very popular in restaurants, or certain species of shrimp and prawn. I’ve seen clients have great success with species like the Pacific White Shrimp. They are hardy and grow quickly in a controlled environment. The choice depends on your local market demand and your capacity to manage their specific needs. Starting with a resilient species is a smart move for anyone new to saltwater aquaculture. It allows you to learn the ropes before moving on to more sensitive, and potentially more profitable, varieties.
| Feature | Traditional Ocean Farming4 | Inland Saltwater Farming5 |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Coastal areas, open sea | Anywhere with space and water |
| Control | Low (subject to weather, tides) | High (controlled environment) |
| Predators | High risk | Low to no risk |
| Water Quality | Variable | Stable and managed |
What does adding salt to a pond do?
Your pond is a freshwater ecosystem, which is a completely different world for a sea fish. But a simple, common ingredient can change everything. Adding salt is the key to this transformation.
Adding salt to a pond increases its salinity, turning it from a freshwater to a brackish or saltwater environment. This is essential for creating a habitat where sea fish can survive, as it helps regulate their internal fluid balance and protects them from freshwater parasites.
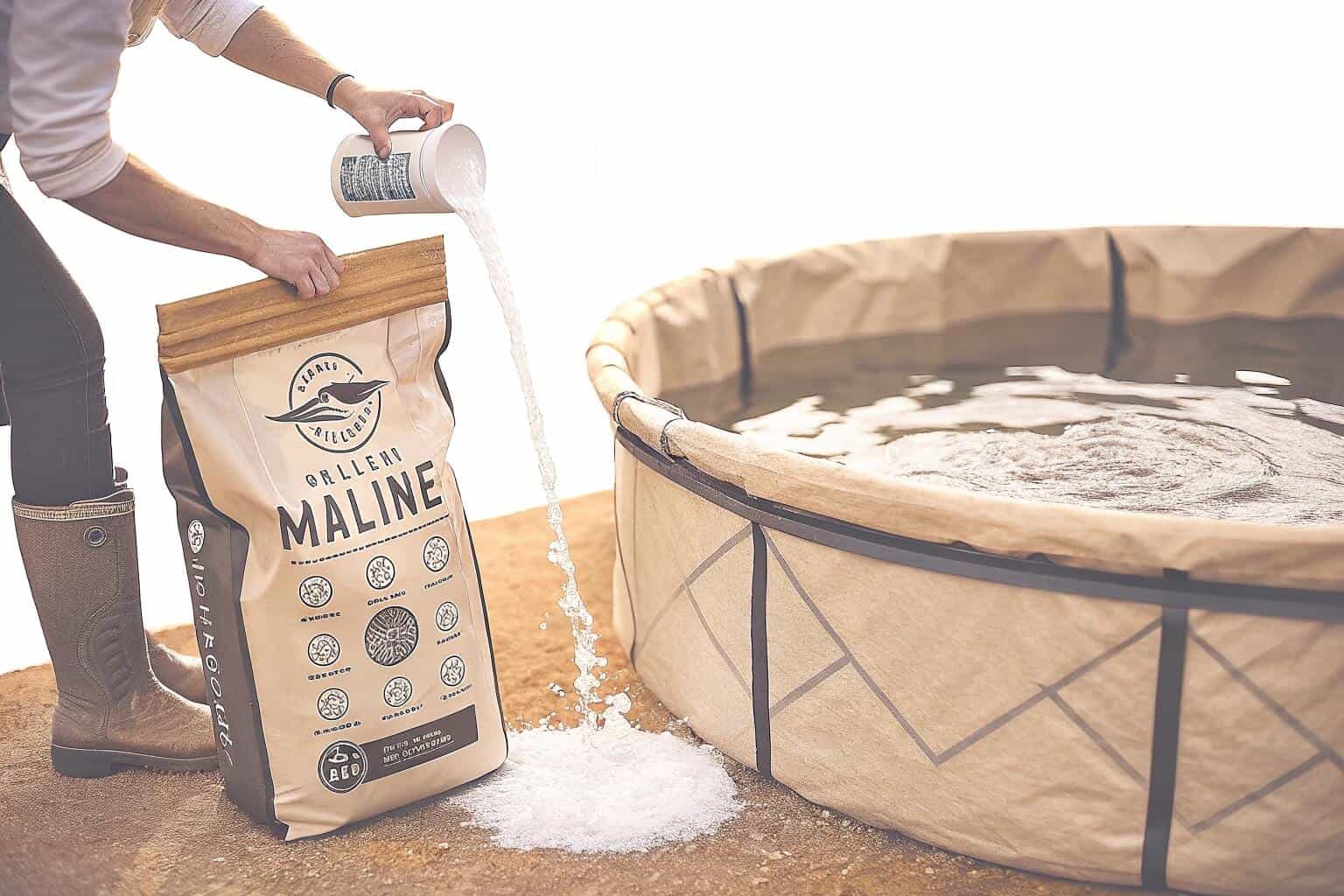

However, simply adding salt isn’t enough. Maintaining the correct salinity level consistently is crucial for the fish’s health and survival. Monitoring equipment is needed to measure and adjust salt concentrations, ensuring the artificial marine environment remains stable and hospitable for your chosen species.
Creating the Right Salinity Level
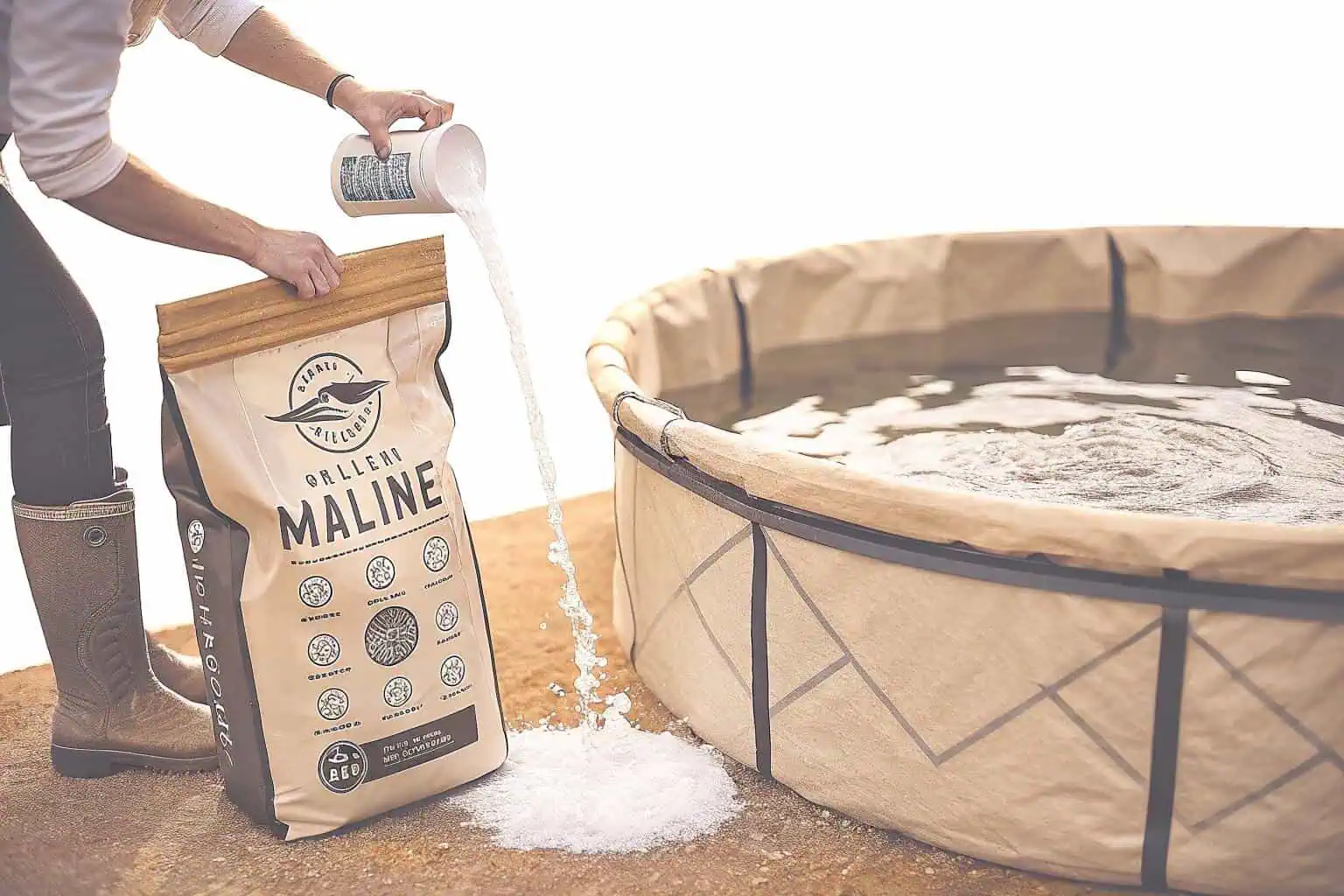
Getting the salt level right is both an art and a science. It’s not just about dumping salt in; it’s about precision. Different fish have different needs. For example, a fish from a brackish estuary will need a lower salinity than one from the deep ocean. You’ll need a tool called a refractometer6 or a salinity meter7 to measure the salt content accurately, usually expressed in parts per thousand (ppt). The ocean is typically around 35 ppt. You must add salt gradually and mix it thoroughly to avoid creating pockets of high concentration that could harm the fish. I always advise my clients to start with a separate mixing tank, like one of our smaller Bancy collapsible water bladders, to prepare the saltwater before adding it to the main fish tank. This ensures a uniform and safe environment for your stock.
Impact on Water Chemistry and Osmoregulation
Adding salt does more than just make the water salty. It fundamentally changes the water’s chemistry. For saltwater fish, this is a matter of life and death. They have a biological process called osmoregulation to manage the salt levels in their bodies. In the ocean, they constantly drink water and excrete excess salt to stay hydrated. In a freshwater environment8, the opposite would happen—water would flood their cells. By creating a saltwater environment in your pond, you allow their bodies to function as they are naturally designed to. This reduces stress on the fish, which in turn improves their health, growth rate, and overall quality. It’s a perfect example of how recreating a natural process is the best approach to farming.
Choosing the Right Type of Salt
Not all salt is created equal. You can’t just use table salt from your kitchen, as it often contains iodine and anti-caking agents that can be toxic to fish. The best choice is a high-quality marine salt mix, the same kind used in saltwater aquariums. These mixes are specifically formulated to replicate the mineral and trace element composition of natural seawater, not just the sodium chloride. This includes essential elements like magnesium and calcium9, which are vital for fish health. While it might be more expensive upfront, investing in the right salt is a critical step. It ensures you are building a healthy, stable foundation for your aquaculture venture. It’s a lesson I’ve learned over years of helping people set up reliable liquid management systems.
| Fish Species | Ideal Salinity (ppt) |
|---|---|
| Barramundi | 15-30 ppt |
| Pacific White Shrimp10 | 20-35 ppt |
| Red Drum | 25-35 ppt |
| Tilapia (some species) | 10-20 ppt |
Can you make a fish that lives in salt water live in pure water?
Fish have very specific biological needs, and their environment is everything. What happens if you ignore their most basic requirement for salt? The outcome is unfortunately predictable and highlights a fundamental rule of nature.
No, you generally cannot make a saltwater fish live in pure freshwater. Their bodies are biologically adapted to high-salinity water. In freshwater, they would suffer from osmotic shock as their cells absorb too much water and rupture, leading to rapid death.
This strict dependency on salinity is why simply placing a saltwater fish in freshwater is fatal. Their internal systems are designed to handle salt concentration gradients, and without the proper saline balance, their bodies fail to function. Understanding this basic physiological barrier is key to any successful attempt at creating a suitable habitat.
Understanding Osmosis in Fish
I remember learning about osmosis in school, and it’s a concept that is incredibly important in my line of work. Osmosis is the movement of water across a membrane from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated one. A saltwater fish’s body fluids are less salty than the surrounding seawater. To combat dehydration, they drink seawater and their gills pump out excess salt. In freshwater, the situation is reversed. The fish’s body is saltier than the water. Water would rush into its cells, causing them to swell and burst. This is why a sealed, controlled environment is so important. You are not just containing water; you are maintaining a delicate biological balance11 that is essential for life.
Why Saltwater Fish Need Salt
Salt is not just a preference for these fish; it’s a structural component of their world. Their entire physiology, from their kidneys to their gills, is built to handle a high-salt environment12. Removing that salt is like removing the oxygen from our air. They simply cannot process freshwater. Their kidneys are not equipped to handle the massive amounts of water that would be absorbed, and their gills would fail. This is a hard biological limit. As a provider of aquaculture equipment, I always stress this point. Our tanks are designed to create the perfect saltwater home, because we understand that there is no substitute for the fish’s native environment.
Are There Any Exceptions?
Nature loves to create exceptions, and this is one of them. Some fish, known as euryhaline species, can tolerate a wide range of salinities. Salmon are a famous example, as they are born in freshwater, migrate to the ocean, and return to freshwater to spawn. Other examples include species like tilapia and barramundi, which can be acclimated to different salt levels. This adaptability makes them excellent candidates for inland aquaculture13. However, even these hardy fish require a careful and gradual acclimation process. You can’t just move them from one extreme to the other. This flexibility is a huge advantage for farmers, but it still requires careful management and a deep respect for the fish’s biology.
| Feature | Saltwater Fish | Freshwater Fish |
|---|---|---|
| Body Fluids14 | Less salty than water | Saltier than water |
| Drinking15 | Drinks constantly | Drinks very little |
| Urine | Concentrated, small amount | Diluted, large amount |
| Gills | Excrete salt | Absorb salt |
Is a saltwater pond possible?
Creating a saltwater pond in your backyard or on your farm might seem like a huge, expensive project. But imagine having a contained, manageable piece of the ocean. With the right technology, it is entirely possible.
Yes, a saltwater pond is definitely possible, especially with modern solutions like durable, leak-proof collapsible tanks. These containers prevent salt from seeping into the ground and allow for precise control over water conditions, making it a very viable option for inland aquaculture.
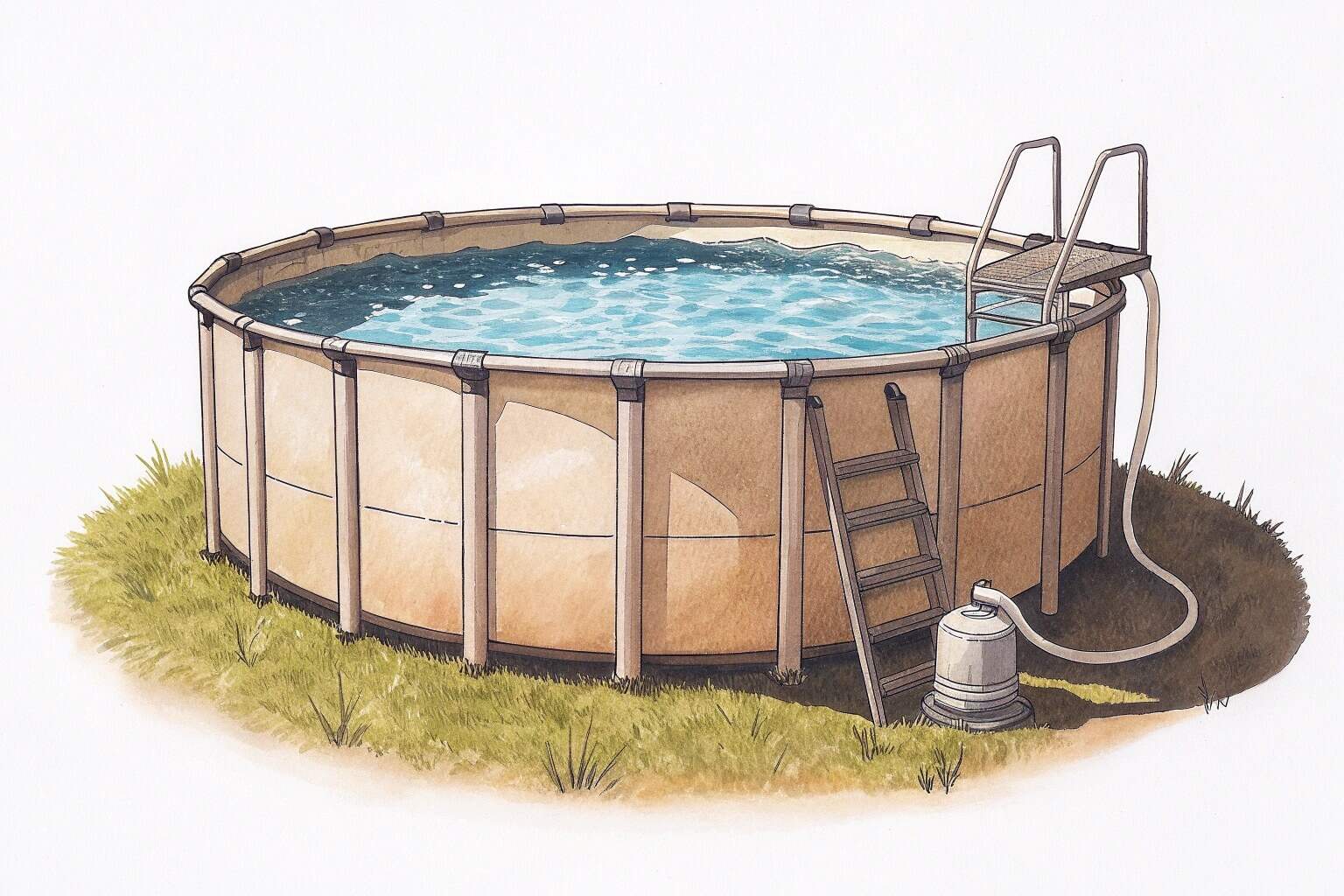
These innovative tank systems represent a significant advancement, moving beyond traditional methods that were often limited by location and cost. They provide a controlled environment where you can replicate oceanic conditions, opening up possibilities for cultivating marine life far from the coast.
The Challenge of Traditional Ponds
If you dig a traditional earthen pond and fill it with saltwater, you will face major problems. First, the salt will seep into the surrounding soil, which can damage the local ecosystem and contaminate groundwater. This is something I care about deeply, as sustainable practice is a core value at Bancy. Second, it’s nearly impossible to maintain a stable salinity level16 in an earthen pond. Rain will dilute it, and evaporation will concentrate it. You will be in a constant battle with nature. Furthermore, the soil itself can introduce unpredictable variables into the water chemistry. For these reasons, a simple hole in the ground is not a practical solution for serious saltwater aquaculture.
Why Collapsible Tanks Are the Ideal Solution
This is where my passion for our products at Bancy comes in. Collapsible fish tanks17 solve all the problems of a traditional pond. They are made from a strong, inert PVC liner that creates a completely closed system. There is no seepage of salt into the ground. The water volume is fixed, making it easy to calculate, monitor, and maintain the exact salinity you need. Our tanks are supported by a sturdy frame, making them durable for long-term use. I am particularly proud of our double-welding technology, which ensures the seams are incredibly strong and leak-proof. This gives our customers the confidence that their investment is secure and their aquatic environment is stable. They are also easy to set up, move, and customize, offering a level of flexibility that is unmatched.
Setting Up Your First Saltwater Tank System
Getting started is straightforward. First, you choose a level spot for your tank. Assembly of our Bancy tanks is simple and doesn’t require special tools. Once the tank is set up, you begin the process of making saltwater, ideally in a separate container before transferring it. You’ll install your filtration system, a pump for water circulation, and a heater if needed. Then, you let the system run for a while to stabilize, a process called cycling. This allows beneficial bacteria to establish, which will break down fish waste. Only after the water parameters are stable and correct should you introduce your fish. It’s a methodical process, but it sets you up for success. We offer customized solutions and can guide our clients through every step, ensuring they have the right setup for their specific goals.
| Feature | Traditional Earthen Pond | Bancy Collapsible Tank |
|---|---|---|
| Seepage18 | High risk of soil contamination | None, fully contained |
| Salinity Control19 | Very difficult | Easy and precise |
| Setup | Labor-intensive excavation | Quick and simple assembly |
| Flexibility20 | Permanent | Portable and customizable |
Conclusion
Farming sea fish inland is no longer a dream. With the right knowledge and modern tools like collapsible tanks, it is a practical and exciting reality for aquaculturists everywhere.
- Explore the advantages of saltwater aquaculture, including sustainability and ecosystem control, to enhance your understanding of this innovative farming method. ↩
- Maintaining water quality is crucial for fish survival and growth. This resource provides valuable insights and techniques for effective management. ↩
- Explore the advantages of Barramundi farming, including market demand and growth potential, to make informed decisions in aquaculture. ↩
- Explore the advantages of Traditional Ocean Farming, including its ecological impact and sustainability practices. ↩
- Learn about the innovative techniques and benefits of Inland Saltwater Farming for sustainable aquaculture. ↩
- Explore this link to understand how a refractometer works and its importance in maintaining the right salinity for fish health. ↩
- Learn about salinity meters and their role in ensuring optimal conditions for aquatic life, crucial for any fish keeper. ↩
- Learn about the challenges fish encounter in freshwater and how it impacts their biology and health, essential for effective fish farming. ↩
- Understanding the role of magnesium and calcium can help you maintain a thriving aquatic environment for your fish. ↩
- Discover the best farming practices for Pacific White Shrimp to maximize yield and sustainability. This link offers expert guidance. ↩
- Discover the importance of biological balance in ecosystems and how it affects all forms of life, ensuring sustainability and health. ↩
- Understanding the impact of high-salt environments on fish can enhance aquaculture practices and fish care. ↩
- Exploring the benefits of inland aquaculture can provide insights into sustainable fish farming practices. ↩
- Understanding the differences in body fluids can help in studying fish physiology and their adaptations to different environments. ↩
- Exploring the drinking habits of these fish reveals their unique adaptations to their habitats and survival strategies. ↩
- Learn effective methods to manage salinity levels, crucial for successful aquaculture operations. ↩
- Explore the advantages of collapsible fish tanks to understand how they can enhance your aquatic setup and solve traditional pond issues. ↩
- Explore how fully contained systems like Bancy Collapsible Tanks eliminate seepage risks, ensuring safer water storage. ↩
- Learn about effective salinity control methods that make water management easier and more precise. ↩
- Discover the benefits of portable and customizable water storage solutions for various applications and needs. ↩







